Ear wax, commonly known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced in the ear canal. The ear serves primarily as a protective barrier, guarding against an array of dirt, dust, and other particles that could potentially damage the sensitive eardrum. While it’s generally recommended to manage earwax, it can sometimes lead to discomfort, itching, and in severe instances, temporary hearing loss. Many people often wonder if certain food products can lead to the production of earwax. The relationship between diet and earwax is a topic that sparks curiosity. Is it a myth or a reality? Let’s delve into the facts to uncover the truth behind this intriguing question.
Understanding Earwax and Its Functions
Earwax comes in two distinct varieties: the wet type, characterised by its reddish-brown, gooey texture, and the dry type, which is hard and white in colour.
Protective Role of Earwax
Means of Protection: They serve as a shield against dust, dirt, and microorganisms, effectively stopping them from reaching the eardrum.
Lubrication: Lubrication serves to keep the skin of the ear canal moist, preventing it from cracking and alleviating itchiness.
Cleaning mechanism: The ear features a remarkable self-cleaning system. It naturally expels wax debris found in the ear canal through movements of the jaw, such as chewing.
Debunking Myths: Foods and Earwax
Let’s explore a few of these myths along with the facts that debunk them.
Dairy Products
Myth: There’s a common belief that consuming dairy products, especially cheese and yoghurt, results in higher earwax production.
Fact: It’s important to note that there is no scientific evidence supporting the idea that dairy products contribute to the production of earwax. It likely stems from rumours and misunderstandings related to how diet affects bodily functions.
Shellfish and Zinc
Myth: There’s a common misconception that fish with shells, especially those containing zinc, can pose a serious risk to health by increasing earwax production.
Fact: Zinc is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in the proper functioning of the body, particularly for the immune system. A lack of zinc can lead to several health issues, but obtaining it from shellfish or supplements won’t result in earwax accumulation. Interestingly, some groups have pointed out that zinc deficiency may lead to reduced earwax production.
Corn and Starches
Myth: Some foods are thought to influence the thickness of earwax, and corn, known for its high starch content, is one of them.
Fact: It’s a common belief that eating starches leads to thicker earwax, but this is simply a myth. There is, in fact, a lack of scientific evidence to back up that claim. It is clear that the consistency of earwax is influenced more by genetics and environmental factors than by an individual’s diet.
Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates
Myth: The belief that consuming a lot of sweets and foods high in refined carbohydrates leads to an overproduction of earwax is a misconception.
Fact: Consuming too much sugar can lead to various harmful effects on our bodies, there is no proof linking it to an increase in earwax production. Consuming a lot of refined sugars can affect overall health, which may subsequently influence bodily functions; however, this is not related to earwax.
Scientific Perspective on Diet and Earwax
While specific foods may not directly contribute to earwax buildup, the overall diet plays a significant role in an individual’s health, which in turn influences earwax production.
Role of Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is crucial for keeping your skin healthy and ensuring the right moisture levels in your ear canal. When dehydration occurs, it leads to a decrease in earwax production. The earwax that does remain can become drier, making it more difficult for the body to naturally expel it from the ear.
Balanced Diet and Health
A well-rounded diet plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and supports the body’s natural processes for producing and eliminating earwax. Vitamins A, D, E, and K, along with Omega-3 fatty acids, play a role in skin and tissue health, which in turn influences the production of earwax.
Possible Allergens and Responses
Individuals with allergies may experience issues related to the colour, texture, or rate of earwax formation. Certain foods that can trigger allergies may cause the body to swell, which in turn could result in changes to earwax. It largely varies from person to person and doesn’t necessarily indicate a straightforward cause-and-effect relationship between the two.
Effective Strategies for Earwax Management
Here are some helpful tips for dealing with earwax issues:
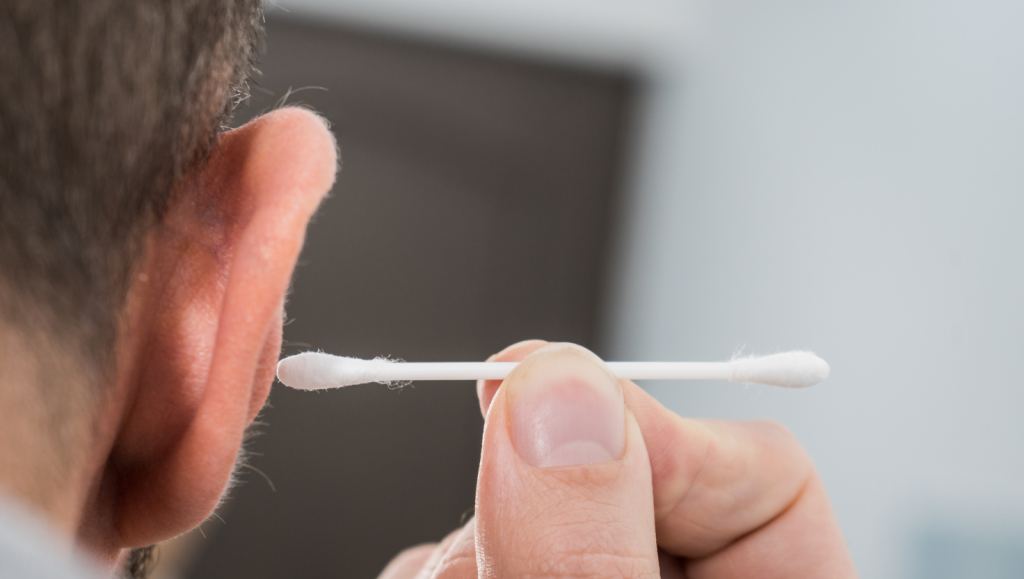
Avoid Inserting Objects
Avoid inserting anything into your ears for cleaning purposes, including cotton swabs or any other objects. In this regard, it may drive earwax deeper into the canal and potentially cause impaction.
Stay Hydrated
To keep earwax at a normal level, it’s important to stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
Seek Guidance from a Healthcare Expert
If you’re feeling discomfort or a sense of blockage in your ears, it’s a good idea to reach out to a doctor for advice. They can also remove any excess ear wax whenever it becomes necessary.
Explore Natural Remedies
Consider using warm olive oil drops, which might assist in softening earwax. It’s important to approach these with caution and to seek guidance from a health professional when necessary.